For Public
අක්මා බද්ධ කිරීම ගැන දැනුවත් වෙමු.
Successful transplantation of a fatty liver
කුඩා දරුවන්ගේ අක්මාව බද්ද කිරීම
COVID 19 රෝගය අක්මා රෝග හා අනෙකුත් දීර්ඝ කාලීන රෝග සදහා ප්රතිකාර ගන්නා රෝගීන්ට බලපාන්නේ කෙසේද?
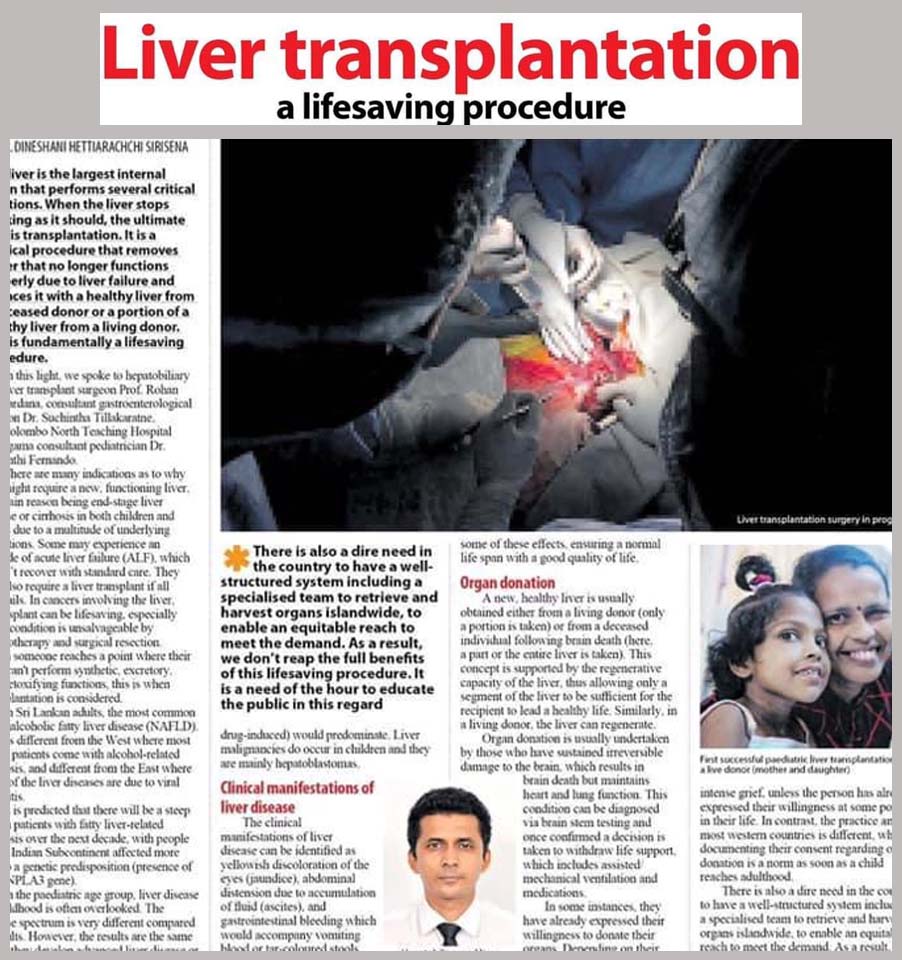
Organ donation & transplantation
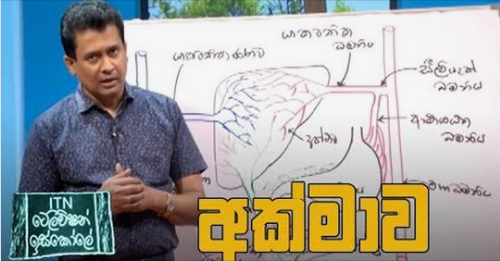
Know about your liver
Cirrhosis of the liver
Bile is made in the liver as a part of the metabolic activity of the body. It consists of waste products of the body and contains enzymes that are important in the digestion of food. The bile excreted from the liver is sent to the duodenum via the biliary tree. The biliary tree consists of multiple small ducts which merge to form the bile duct. The biliary tree can be divided into into a part inside the liver which is called intrahepatic portion and the part outside the liver which is the extrahepatic portion. Gall bladder is a structure attached to the biliary system which helps in storage and release of bile in response to a meal.
Gall bladder removal Surgery - Cholecystectomy
Gallbladder is a small, tear-drop shaped organ located under the liver (see Figure 1). Its main function is to store bile and release in response to a meal. Bile helps in digestion of fat in the food. When your gallbladder is removed the biliary system will takeover this function and there will be no harmful effects on digestion.
Cholecystectomy is the surgery that is performed to remove the gallbladder. The gallbladder can be removed in one of two ways—laparoscopically (keyhole) or through an open incision (surgical cut). Laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery is performed 95% of the time but there may be instances that open surgery with larger surgical cut has to be performed.
In laparoscopic surgery four small incisions less than 1 cm will be made in the abdomen and the gallbladder will be taken out through one of the incisions after the dissection. This is generally done as a day procedure and patient is discharged within 24 hours most of the time. Open surgery may need additional hospital stay for the management of pain.
Figure 2. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy incisions
Figure 3. Open cholecystectomy incision
One of the incisions will be in or near your navel (belly button). Your surgeon will insert an instrument called a laparoscope through this incision. The laparoscope is a thin tube that has a video camera at the tip. Carbon dioxide gas is blown into your abdomen (belly) so that it expands. This makes room for your surgeon to see your organs and tissues. Other instruments will be inserted through three other incisions to help to remove your gallbladder. Your gallbladder will then removed through an incision at your navel. The laparoscopic gallbladder removal surgery takes about 1 to 2 hours.
Open surgery
In about 5% of cases, the gallbladder needs to be removed through a larger incision on your abdomen. This surgery takes about 2 hours. This is done generally when the surgery is difficult, and it is no longer safe to do it laparoscopically.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the standard procedure in most patients. Symptomatic gallstones: either due to acute or chronic inflammation or biliary colic are the usual indications. Biliary colic usually presents with right sided recurrent pain. Chronic cholecystitis usually gives rise to symptoms to gastritis. Acute cholecystitis the pain is associated with fever.
Cholecystectomy sometimes can be complicated. Injury to the biliary system is one of the feared complications. It can vary from simple bile leak to completed cut off to the biliary tree. Bile duct injury must be manged in a specialised centre for a good outcome.
Bile duct injuries
Bile duct injuries has become a serious concern in laparoscopic cholecystectomy Proper training and extreme care can reduce the risk of this unfortunate complication. According to literature the incidence is around 0.05%. the degree of injury can vary from simple bile leak to complete damage of the bile duct. North Colombo Centre for liver diseases (CNCLD) gets many referrals with bile duct injuries. We have the state-of-the-art facilities including interventional radiology, ERCP for comprehensive management of such bile duct injuries. We are more inclined towards immediate repair of bile duct injuries compared to delayed approach in some canters.
Choledochal cyst
Choledochal cysts are abnormal dilatation in the biliary tree without a significant distal obstruction. They present with abdominal discomfort pain or fever and occasionally jaundice. These carry a risk of malignancy towards the latter part of life. Due to this surgical excision and reconstruction of the biliary drainage system is recommended in them. After removing the dilated part of the bile duct small bowel is used to create an anastomosis for the biliary drainage.
Tumours in the biliary tree
Commonest type of cancer in the biliary tree are cholangiocarcinomas. They are very aggressive type of a cancer. Usual presentation is yellowish discoloration of eyes without pain. Surgical resection is the best treatment in them as it gives a chance of cure. All the other treatment are intended to relieve symptoms.
Colombo North Centre for Liver Diseases,
Faculty of Medicine,
University of Kelaniya,
P.O Box 6,
Thalagolla Road,
Ragama, Sri Lanka
Quick Links
Follow Us
Email : cncld@kln.ac.lk